|
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Adult, 3,300 ft., Tehachapi Mountains, Kern County |
 |
 |
 |
| Underside of adult, Tehachapi Mountains, Kern County |
Adult, 3,300 ft. Tehachapi Mountains, Kern County |
 |
 |
 |
| Adult, in defensive pose, 6,000 ft. elevation, Kern County |
 |
 |
 |
| Adult, 6,000 ft. elevation Kern County |
Adult, 1,800 ft. elevation, Kern County, from intergrade zone with E. e. platensis. |
Adult, 4,500 ft., Tehachapi, Kern County.
This Ensatina with large blotches was discovered one night in late December on a back porch. It was 45 degrees and raining. © Terri Asher
|
 |
 |
 |
| Adult, Kern County © Spencer Riffle |
Adult, Kern County © Spencer Riffle |
Adult, Kern County © Spencer Riffle |
 |
 |
 |
| Adult, Kern County © Spencer Riffle |
Adult, Kern County © Spencer Riffle |
Adult, Kern County © Spencer Riffle |
 |
 |
 |
| Adult, Kern County © Zeev Nitzan Ginsburg |
Left: E. e. croceater
Right: E. e. platensis
These two Ensatina were found within a hundred feet of each other in Kern County, where both subspecies occur.
© Ryan Sikola |
| |
|
|
Juveniles |
 |
 |
 |
Juvenile, 6,000 ft.,
Kern County |
Juvenile, 3,300 ft. Tehachapi Mountains, Kern County |
Juvenile, (about 1.5 inches in length) Tehachapi Mountains, Kern County |
| |
|
|
| Hybrids or Intergrades |
 |
 |
 |
Pale-blotched adult, (probably an intergrade with the Large-blotched
Ensatina) 5,500 ft., Mt. San Jacinto, Riverside County |
Adult with the markings of E. e. platensis and the coloring of E. e. croceater,
Kern County © Ryan Sikola |
| |
|
|
| Habitat |
 |
 |
 |
Habitat, 3300 ft., Tehachapi Mountains,
Kern County
|
Habitat, 3300 ft., Tehachapi Mountains,
Kern County |
Habitat, 3,500 ft., Tehachapi Mountains, Kern County |
 |
 |
|
Habitat, 2,400 ft., Kern County
|
Habitat, 6,000 ft., Kern County |
|
| |
|
|
| Short Video |
| |
 |
|
| |
An adult Yellow-blotched Ensatina crawls around on a fallen log trying to get back under cover. |
|
|
|
|
| Description |
| |
| Size |
An adult Ensatina measures from 1.5 - 3.2 inches long (3.8 - 8.1 cm) from snout to vent, and 3 - 6 inches (7.5 - 15.5 cm) in total length.
|
| Appearance |
A medium-sized salamander.
The legs are long, and the body is relatively short, with 12 - 13 costal grooves.
Nasolabial grooves are present.
The tail is rounded and constricted at the base, which will differentiate this salamander from its neighbors.
|
| Color and Pattern |
| This subspecies has a black ground color is marked with large yellow or cream-colored blotches, with yellow or orange on the base of the limbs. |
| Male / Female Differences |
Males have longer, more slender tails than females, and a shorter snout with an enlarged upper lip, while the bodies of females are usually shorter and fatter than the bodies of males.
|
| Life History and Behavior |
A member of family Plethodontidae, the Plethodontid or Lungless Salamanders.
Plethodontid salamanders do not breathe through lungs. They conduct respiration through their skin and the tissues lining their mouth. This requires them to live in damp environments on land and to move about on the ground only during times of high humidity. (Plethodontid salamanders native to California do not inhabit streams or bodies of water but they are capable of surviving for a short time if they fall into water.)
Plethodontid salamanders are also distinguished by their nasolabial grooves, which are vertical slits between the nostrils and upper lip that are lined with glands associated with chemoreception.
All Plethodontid Salamanders native to California lay eggs in moist places on land.
The young develop in the egg and hatch directly into a tiny terrestrial salamander with the same body form as an adult.
(They do not hatch in the water and begin their lives as tiny swimming larvae breathing through gills like some other types of salamanders.)
|
| Activity |
Ensatina live in relatively cool moist places on land becoming most active on rainy or wet nights when temperatures are moderate. They stay underground during hot and dry periods where they are able to tolerate considerable dehydration. They may also continue to feed underground during the summer months. High-altitude populations are also inactive during severe winter cold.
Adults have been observed marking and defending territories outside of the breeding season. |
| Territoriality |
| Adults have been observed marking and defending territories outside of the breeding season. |
| Longevity |
| Longevity has been estimated at up to 15 years. |
| Defense |
When it feels severely threatened by a predator, an Ensatina may detach its tail from the body to distract the predator. The tail moves back and forth on the ground to attract the predator while the Ensatina slowly crawls away to safety. The tail can be re-grown.
The tail also contains a high density of poison glands. When disturbed, an Ensatina will stand tall in a stiff-legged defensive posture with its back swayed and the tail raised up while it secretes a milky white substance from the tail, swaying from side to side. This noxious substance repels predators, although some experienced predators learn to eat all but the tail. The poison is also exuded from glands on the head.
If a person gets the poison on their lips, they will experience some numbness for several hours.
(Charles Brown - Ensatina.net)
Rarely, an Ensatina may make a hissing or squeaking sound when threatened.
|
| Predators |
Predators include Stellar's Jays, gartersnakes, and racoons.
(Kuchta and Parks, Lanoo ed. - Amphibian Declines... 2005) |
| Diet and Feeding |
Ensatinas eat a wide variety of invertebrates, including worms, ants, beetles, spiders, scorpions, centipedes, millipedes, sow bugs, and snails.
They expell a relatively long sticky tongue from the mouth to capture the prey and pull it back into the mouth where it is crushed and killed, then swallowed.
Typically feeding is done using sit-and-wait ambush tactics, but sometimes Ensatinas will slowly stalk their prey. |
| Sound |
"Rarely, it may produce a squeak or snakelike hiss, quite a feat for an animal without lungs!"
(Stebbins & McGinnis 2012)
|
 |
This frightened Humboldt County Ensatina is raised up in defensive mode, excreting a milky white defensive liquid on its head and tail. It jerks its head several times, and each time it makes a very faint squeaking sound.
Click the picture to play a short video to hear the squeaking. (You might need to turn the volume all the way up.)
© Cory Walker |
| Reproduction |
Reproduction is terrestrial.
Mating takes place in Fall and Spring, but may also occur throughout the winter.
Stebbins describes an elaborate Ensatina courtship involving the male rubbing his body and head against the female eventually dropping a sperm capsule onto the ground which the female picks up with her cloaca. You can watch an Ensatina courtship video on YouTube.
The female can store the sperm until she determines the time is right to fertilize her eggs.
At the end of the rainy season, typically April or May, females retreat to their aestivation site under bark, in rotting logs, or in underground animal burrows, and lay their eggs. |
| Eggs |
Females lay 3 - 25 eggs, with 9 - 16 being average.
Females remain with the eggs to guard them until they hatch.
(Pictures of Ensatinas with their eggs and hatchlings)
In labs, eggs have hatched in 113 - 177 days. |
| Young |
Young develop completely in the egg and hatch fully formed.
Young probably leave the nesting site with the first saturating Fall rains, or, at higher elevations, after the snow melts.
|
| Habitat |
Found in evergreen and deciduous forests, under rocks, logs, and other surface debris, especially bark that has peeled off and fallen beside decaying logs. Shaded north-facing areas seem to be favored, especially near creeks or streams.
Most common where there is a lot of woody debris on the forest foor. In dry or very cold weather, stays inside moist logs, animal burrows, under roots, woodrat nests, and under rocks.
|
| Geographical Range |
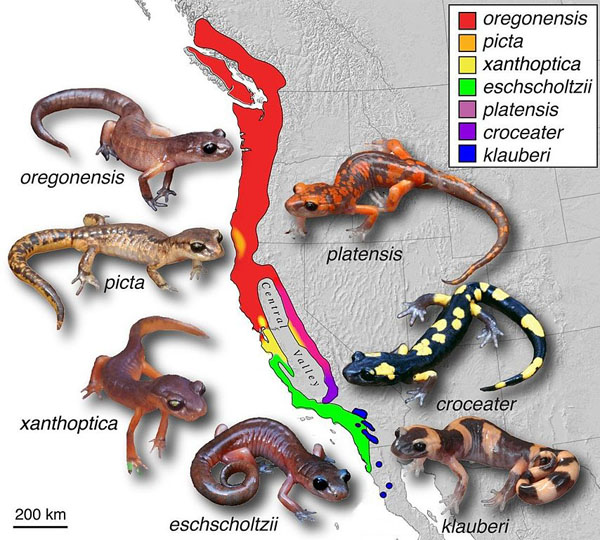
Yellow-blotched Ensatina are endemic to California. They occur in the lower Kern River Canyon, the Paiute Mountains, Breckenridge Mountain, the Tehachapi mountains, on Mt. Abel, Mt. Pinos, near Fort Tejon, and near Frazier-Alamo mountain. Some individuals in the lower Kern River Canyon are intergrades with E. e. platensis. Intergrades with E. e. klauberi are found in the San Bernardino and San Jacinto Mountains.
Ensatina is the most widely-distributed plethodontid salamander in the West, ranging from an isolated location in the mountains of Baja California north along the extreme northwest coast of Baja California, through most of California excluding the deserts, the central valley, and high elevations in the mountains, continuing north into Oregon and Washington west of the Cascades Mountains, and farther north into Canada along the coast of southern British Columbia. Also found on Vancouver Island.
The range maps in Stebbins (2003 and 2012) show a very large range of intergradation between 4 subspecies in Northern California that at one time was considered part of the range E. e. oregonensis. I show this range on my maps as E. e. oregonensis partly because Stebbins & McGinnis, 2012, report that molecular studies have shown complexities that make the use of the term "intergrade" inaccurate.
|
 |
| Elevational Range |
In his 2003 field guide, Stebbins shows the elevational range of Ensatina eschscholtzii as "Sea level to around 11,000 ft (3,350 m). That is for the species but not necessarily this subspecies.
|
| Notes on Taxonomy |
Ensatina taxonomy is controversial. The species Ensatina eschscholtzii traditionally consists of 7 subspecies:
E. e. croceater
E. e. eschscholtzii
E. e. klauberi
E. e. oregonensis
E. e. picta
E. e. platensis
E. e. xanthoptica
Some researchers see Ensatina eschscholtzii as two or more species that make up a superspecies complex.
They recognize E. e. klauberi, found at the southern end of the ring, as a separate species - Ensatina klauberi.
Ensatina as a Ring Species
Ensatina eschscholtzii has been called a "ring" species, or "Rassenkreis" (race circle) "...a connected series of neighbouring populations, each of which can interbreed with closely sited related populations, but for which there exist at least two 'end' populations in the series, which are too distantly related to interbreed, though there is a potential gene flow between each 'linked' population. Such non-breeding, though genetically connected, 'end' populations may co-exist in the same region thus closing a 'ring'." (Wikipedia, 8/26/17) The "end" populations of Ensatina are the E. e. escholtzii and the E. e. klauberi subspecies, which hybridize in San Diego County.
To learn much more about Ensatina and the ring species concept, check out this Understanding Evolution Research Profile about Tom Devitt's work.
Charles W. Brown explains the taxonomy of the Ensatina complex in detail, describing it as "a classical example of Darwinian evolution by gradualism; an accumulation of micro mutations that is now leading to the formation of a new species."
Illustration of the Ensatina ring:
Use: This file is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 2.0 Generic license.
Photo Credit: Thomas J. Devitt, Stuart J.E. Baird and Craig Moritz, 2011.
Source: (2011). "Asymmetric reproductive isolation between terminal forms of the salamander ring species Ensatina eschscholtzii revealed by fine-scale genetic analysis of a hybrid zone". BMC Evolutionary Biology 11 (1): 245. DOI:10.1186/1471-2148-11-245.
Alternate and Previous Names (Synonyms)
Ensatina eschscholtzii croceater - Yellow-blotched Ensatina (Stebbins 2003, 2012)
Ensatina eschscholtzii croceater - Yellow-blotched Salamander (Ensatina) (Stebbins 1966, 1985)
Ensatina eschscholtzii croceater - ssp. of Eschscholtz's Salamander (Stebbins 1954)
Ensatina croceater - YellowBlotched Salamander (Yellow Spotted Salamander) (Bishop 1943)
Ensatina croceater - Yellow-spotted Salamander - (Storer 1925)
Plethodon croceater - Yellow-spotted Salamander - Cape St. Lucas Triton, Yellow-spotted Lizard (Grinnell and Camp 1917)
Plethodon croceater (Cope 1867)
|
| Conservation Issues (Conservation Status) |
| This subspecies is a species of special concern. |
|
| Taxonomy |
| Family |
Plethodontidae |
Lungless Salamanders |
Gray, 1850 |
| Genus |
Ensatina |
Ensatinas |
Gray, 1850 |
| Species |
Eschscholtzii |
Ensatina |
Gray, 1850 |
Subspecies
|
croceater |
Yellow-blotched Ensatina |
(Cope, 1867) |
|
Original Description |
Ensatina eschscholtzii - Gray, 1850 - Cat. Spec. Amph. Coll. Brit. Mus., Batr. Grad., p. 48
Ensatina eschscholtzii croceater - Cope, "1867" 1868 - Proc. Acad. Nat. Sci. Philadelphia, Vol. 19, p. 210
from Original Description Citations for the Reptiles and Amphibians of North America © Ellin Beltz
|
|
Meaning of the Scientific Name |
Ensatina - Latin - ensatus = sword shaped + -ina = similar to, possibly referring to the teeth
eschscholtzii - honors Johann F. Eschscholtz
croceater - Latin = saffron colored & black, referring to the color pattern of the subspecies
from Scientific and Common Names of the Reptiles and Amphibians of North America - Explained © Ellin Beltz
|
|
Related California Salamanders |
Large-blotched Ensatina
Monterey Ensatina
Oregon Ensatina
Painted Ensatina
Sierra Nevada Ensatina
Yellow-blotched Ensatina
|
|
More Information and References |
California Department of Fish and Wildlife
AmphibiaWeb
Hansen, Robert W. Kern River Research Area Field Notes Spring 1997 Vol. 6, No. 2
Hansen, Robert W. and Shedd, Jackson D. California Amphibians and Reptiles. (Princeton Field Guides.) Princeton University Press, 2025.
Stebbins, Robert C., and McGinnis, Samuel M. Field Guide to Amphibians and Reptiles of California: Revised Edition (California Natural History Guides) University of California Press, 2012.
Stebbins, Robert C. California Amphibians and Reptiles. The University of California Press, 1972.
Flaxington, William C. Amphibians and Reptiles of California: Field Observations, Distribution, and Natural History. Fieldnotes Press, Anaheim, California, 2021.
Nicholson, K. E. (ed.). 2025. Scientific and Standard English Names of Amphibians and Reptiles of North America North of Mexico, with Comments Regarding Confidence in Our Understanding. Ninth Edition. Society for the Study of Amphibians and Reptiles. [SSAR] 87pp.
Samuel M. McGinnis and Robert C. Stebbins. Peterson Field Guide to Western Reptiles & Amphibians. 4th Edition. Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company, 2018.
Stebbins, Robert C. A Field Guide to Western Reptiles and Amphibians. 3rd Edition. Houghton Mifflin Company, 2003.
Behler, John L., and F. Wayne King. The Audubon Society Field Guide to North American Reptiles and Amphibians. Alfred A. Knopf, 1992.
Robert Powell, Roger Conant, and Joseph T. Collins. Peterson Field Guide to Reptiles and Amphibians of Eastern and Central North America. Fourth Edition. Houghton Mifflin Harcourt, 2016.
Powell, Robert., Joseph T. Collins, and Errol D. Hooper Jr. A Key to Amphibians and Reptiles of the Continental United States and Canada. The University Press of Kansas, 1998.
American Museum of Natural History - Amphibian Species of the World 6.2
Bartlett, R. D. & Patricia P. Bartlett. Guide and Reference to the Amphibians of Western North America (North of Mexico) and Hawaii. University Press of Florida, 2009.
Bishop, Sherman C. Handbook of Salamanders. Cornell University Press, 1943.
Lannoo, Michael (Editor). Amphibian Declines: The Conservation Status of United States Species. University of California Press, June 2005.
Petranka, James W. Salamanders of the United States and Canada. Smithsonian Institution, 1998.
Joao Alexandrino, Stuart J. E. Baird, Lucinda Lawson, J. Robert Macey, Craig Moritz, and David B. Wake. Strong Selection Against Hybrids at a Hybrid Zone in the Ensatina Ring Species Complex and Its Evolutionary Implications. Evolution, 59(6), 2005, pp. 1334–1347.
Shawn R. Kuchta, Duncan S. Parks, David B. Wake. Pronounced phylogeographic structure on a small spatial scale: Geomorphological evolution and lineage history in the salamander ring species Ensatina eschscholtzii in central coastal California. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution 50 (2009) 240–255
Joseph Grinnell and Charles Lewis Camp. A Distributional List of the Amphibians and Reptiles of California. University of California Publications in Zoology Vol. 17, No. 10, pp. 127-208. July 11, 1917.
|
|
|
The following conservation status listings for this animal are taken from the April 2024 State of California Special Animals List and the April 2024 Federally Listed Endangered and Threatened Animals of California list (unless indicated otherwise below.) Both lists are produced by multiple agencies every year, and sometimes more than once per year, so the conservation status listing information found below might not be from the most recent lists. To make sure you are seeing the most recent listings, go to this California Department of Fish and Wildlife web page where you can search for and download both lists:
https://www.wildlife.ca.gov/Data/CNDDB/Plants-and-Animals.
A detailed explanation of the meaning of the status listing symbols can be found at the beginning of the two lists. For quick reference, I have included them on my Special Status Information page.
If no status is listed here, the animal is not included on either list. This most likely indicates that there are no serious conservation concerns for the animal. To find out more about an animal's status you can also go to the NatureServe and IUCN websites to check their rankings.
Check the current California Department of Fish and Wildlife sport fishing regulations to find out if this animal can be legally pursued and handled or collected with possession of a current fishing license. You can also look at the summary of the sport fishing regulations as they apply only to reptiles and amphibians that has been made for this website.
The 2021 Special Animals List uses a different common name for this subspecies than is used here:
yellow-blotched salamander
|
| Organization |
Status Listing |
Notes |
| NatureServe Global Ranking |
G5T3 |
Species: Secure—Common |
| NatureServe State Ranking |
S3 |
Vulnerable |
| U.S. Endangered Species Act (ESA) |
None |
|
| California Endangered Species Act (CESA) |
None |
|
| California Department of Fish and Wildlife |
WL |
Watch List |
| Bureau of Land Management |
S |
Sensitive |
| USDA Forest Service |
S |
Sensitive |
| IUCN |
Not listed |
|
|
|
|







































