|
 |
 |
| Adult, Santa Clara County |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Adult, Santa Clara County |
Adult, Santa Clara County |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Adult, Contra Costa County |
Adult, Santa Cruz County |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| |
Adult, Contra Costa County |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Adults, Alameda County, from the group shown to the right. |
8 adults in situ found under one board, Alameda County |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Adult, Santa Cruz County |
Adult, Contra Costa County |
Adult, Contra Costa County |
Adult, San Francisco County
© Luke Talltree |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Adult, San Francisco County
© Zachary Lim |
Adult, Diablo Range, Alameda County
© Noah Morales |
Adult, Napa County, © Edgar Ortega |
Adult, from eastern Lake County, a probable intergrade with
D. p. occidentalis. © Nancy Mittasch |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Adult, San Francisco County
© Zachary Lim |
Adult, San Francisco County
© Zachary Lim |
Adult, Contra Costa County
© Ryan Dugan |
Two adults found under the same rock in Santa Cruz County © Faris K |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Adult, Solano County © Lou Silva |
Adult, San Mateo County © Mark Gary |
Adult, Santa Clara County © Yuval Helfman |
 |
|
|
|
| Adult, San Mateo County © Zach Lim |
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
| Juveniles |
 |
 |
 |
|
This tiny juvenile from Alameda County makes nice finger jewelry.
© Mandy Colombo Murphy |
Juvenile, Santa Cruz County |
Large juvenile, Alameda County, found surface active in daylight,
© Yuval Helfman |
|
| |
|
|
|
| Pacific Ring-necked Snakes With Unusual Coloring |
 |
 |
 |
 |
This Santa Clara County juvenile snake is melanistic, lacking its normal colors while having an abnormal amount of dark pigment. It appears to be a ring-necked snake, however when color and pattern are removed and only a few pictures are available, small colubrid snakes such as this one are difficult to differentiate from other similar species found in the same area. The other possible species in this case are the Western Black-headed Snake and the Common Sharp-tailed Snake. We ruled out the sharp-tailed snake because of the tail length, and the black-headed snake because of the way the tail is coiled.
© Nathan Hickson |
This melanistic adult was found in Santa Clara County. Four slightly-orange scales are visible on the neck where the ring would normally be.
© Faris K |
 |
 |
 |
|
Unusually-colored adult from Petaluma in Sonoma county. Compare the lack of red pigment on its underside to other snakes on this page.
© Richard Porter
YouTube video.
|
This Pacific Ring-necked Snake found in Alameda County has an unusual underside that is orange and yellow like a ring-necked snake, but with black bars like a sharp-tailed snake. © Faris K |
|
| |
|
|
|
| Ring-necked Snakes Feeding |
 |
 |
 |
 |
An adult San Bernardino Ring-necked Snake eating an adult Arboreal Salamander in Los Angeles County © Jonathan Benson |
Adult Monterey Ring-necked Snake eating a Slender Salamander,
San Luis Obispo County
© Andrew Harmer |
A Pacific Ring-necked Snake eating a California Slender Salamander in Marin County © Andre Giraldi |
 |
 |
 |
|
| Ring-necked Snakes use a mild venom to subdue their prey which include snakes and lizards. This San Diego Ring-necked Snake from San Diego County regurgitated a California Legless Lizard that it had recently eaten. © Donald Schultz |
|
| |
| Habitat |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Habitat, Contra Costa County |
Habitat, Santa Clara County |
Habitat, Santa Cruz County |
Habitat, Contra Costa County |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Habitat, SF Bay, Alameda County |
Habitat, Santa Cruz County |
Habitat, Contra Costa County |
Habitat, Alameda County
© Mandy Colombo Murphy |
| |
|
|
|
| Short Videos - Including Other Subspecies of Ring-necked Snakes |
 |
 |
 |
|
| A Pacific Ring-necked Snake is found under a log in the woods and is filmed on an old picnic table before being released to crawl back under its log. |
A Pacific Ring-necked Snake is found under a board in a forest clearing and demonstrates how quickly it can move. |
A Pacific Ring-necked Snake is found under some trash in Santa Clara County, then another one is uncovered in Santa Cruz County. |
|
 |
 |
|
|
| A San Diego Ring-necked snake is released back where it was found. |
A few brief views of a large San Diego Ring-necked snake and its habitat. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Description |
Not Dangerous - This snake may produce a mild venom that does not typically cause death or serious illness or injury in most humans, but its bite should be avoided.
Commonly described as "harmless" or "not poisonous" to indicate that its bite is not dangerous, but "not venomous" is more accurate since the venom is not dangerous. (A poisonous snake can hurt you if you eat it. A venomous snake can hurt you if it bites you.)
Rear teeth on the upper jaw are enlarged but not grooved which may aid in injecting mild venom into small prey.
|
| Size |
The typical total length of an adult Ring-necked snake (Diadophis punctatus) varies somewhat by subspecies but in general it is about 11 - 16 inches (28 - 42 cm.)
Hatchlings are much smaller and longer specimens are sometimes found.
The record length is 33-5/8 inches (85.4 cm.)
|
| Appearance |
| A small, thin snake with smooth scales. |
| Color and Pattern |
Gray, blue-gray, blackish, or dark olive dorsal coloring, with a yellow to orange underside, speckled with numerous black markings.
The underside of the tail is a bright reddish orange.
A narrow orange band around the neck, 1 - 1.5 scale rows wide.
|
| Similar Species |
From Contra Costa County south to San Diego County California Black-headed Snakes and Ring-necked Snakes might be found in the same location.
Both are small slender long-tailed snakes with a ring around the neck and red coloring on the belly.
Click the photo below to learn how to tell them apart easily.

|
| Life History and Behavior |
Activity |
| Secretive - usually found under the cover of rocks, wood, bark, boards and other surface debris, but occasionally seen moving on the surface on cloudy days, at dusk, or at night. |
| Defense |
When disturbed, coils its tail like a corkscrew, exposing the underside which is usually bright red.
It may also smear musk and cloacal contents. |
| Diet and Feeding |
| Eats slender salamanders and other small salamanders, tadpoles, small frogs, small snakes, lizards, worms, slugs, and insects. The mild venom may help to incapacitate prey. |
| Reproduction |
Females are oviparous, laying eggs in the summer, sometimes in a communal nest.
|
| Habitat |
Prefers moist habitats, including wet meadows, rocky hillsides, gardens, farmland, grassland, chaparral, mixed coniferous forests, woodlands.
|
| Geographical Range |
This subspecies, Diadophis punctatus amabilis - Pacific Ring-necked Snake, is endemic to California, occurring from just north of the San Francisco Bay around Sonoma County, south to the Monterey Bay region.
The species Diadophis punctatus - Ring-necked Snake, has a very wide range, occurring along the entire east coast of the United States west to the Great Lakes and southwest from there through the Midwest into Arizona, with scattered isolated populations throughout most of the western states including the western half of California, Oregon west of the Cascades, and south central Washington.
|
 |
| Notes on Taxonomy |
Based on research published in 2021,
it appears that Diadophis punctatus is composed of several distinct lineages that do not follow the geographic ranges of the subspecies. Showing seven subspecies of Diadophis punctatus in California
appears to be inaccurate now, but since it is closer to the newer three or four species interpretation than it would be to show them all as one species, I will continue to show these seven subspecies until someone formally describes them as three or four species.
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
For years many herpetologists have not recognized the traditional morphologically-based subspecies of Diadophis punctatus (including seven found in California) pending a thorough molecular study of the whole species. One ongoing study (Feldman and Spicer, 2006, Mol. Ecol. 15:2201-2222) has found all of the D. punctatus subspecies in California (except D. p. regalis) to be indistinguishable.
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
In their 2025 field guide, Hansen and Shedd adopt "...the subspecies arrangement proposed in a paper by Fontanella et al. (2021). Those authors examined geographic variation in Pacific Coast ring-necked snakes using both nuDNA and mtDNA sequences, finding that California populations fall into three groups, or subspecies, in addition to the highly distinctive Regal Ringneck Snake (D. p. regalis)." ... "Characters such as color pattern and scale counts, historically used to diagnose subspecies of ringneck snakes, have proven to be unreliable across California populations. An updated scheme for field identification of subspecies is needed."
In this arrangement, the rames and (tentative) ranges of most of the seven subspecies currently shown on this website are changed:
- D. p. amabilis retains the same name but its range now includes the ranges of D. p. occidentalis and D. p. vandenburghii.
- D. p. modestus retains the Latin name - with the common name Southern California Ring-necked snake and the range now includes the range of D. p. similis.
- D. p. occidentalis becomes D. p. amabilis - Pacific Ring-necked Snake
- D. p. pulchellus retains the same name and range
- D. p. regalis retains the same name and range
- D. p. similis becomes D. p. modestus - Southern California Ring-necked Snake
- D. p. vandenburghii becomes D. p. amabilis - Pacific Ring-necked Snake
|
This is a tentative range map of the four subspecies arrangement of
Ring-necked Snakes found in California (based on Hansen and Shedd 2025)
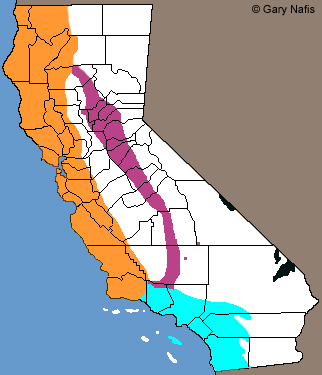
|
Orange - D. p. amabilis - Pacific Ring-necked Snake
(Includes the former subpsecies D. p. vandenburgii and D. p. occidentalis)
Bright Blue - D. p. modestus - Southern California Ring-necked Snake
(Includes the former subspecies D. p. similis)
Purple - D. p. pulchellus - Coral-bellied Ring-necked Snake
Black - D. p. regalis - Regal Ring-necked Snake |
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
In a phylogeographic analysis of the species, Fontanella, et. al (2008) identified fourteen lineages of Diadophis punctatus. They did not recognize these lineages as separate species, pending a full taxonomic review that will require further dna sampling and evaluation, including populations in Mexico.
In our area, they recognized four distinct lineages, which loosely follow existing subspecies boundaries, but merge the seven subspecies into 4 groups:
1 - A southern California lineage, which includes the San Diego and San Bernardino subspecies, D. p. similis, and D. p. modestus.
2 - An eastern California lineage, which includes the Coral-bellied subspecies, D. p. pulchellus, and some of the northern intergrades with D. p. occidentalis.
3 - A Coastal California lineage, which includes the Monterey subspecies, D. p. vandenburghi, the Pacific subspecies, D. p. amabilis, the Northwestern subspecies, D. p. occidentalis, and snakes from one region of the western Sierra Nevada currently recognized as D. p. pulchellus, along with the southern intergrades in the Tehachapi mountains region.
4 - A Great Basin lineage which presumably includes the Regal subspecies, D. p. regalis, found in isolated locations in the eastern Mojave desert.
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Using new samples, nuclear genes, and morphology, Fontanella, et al, (2021), confirmed the three California lineages (not including D. p. regalis) shown in the mtDNA study of Fontanella, et al in 2008, described above, and implied that they are species-level taxa, but they did not formally describe them as new taxa.
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Following the 2008 Fontanella, et al. study, The 2025 SSAR Names List recognizes four subspecies of Diadophis punctatus in California:
D. p. amabilis - Pacific Ring-necked Snake
D. p. modestus - San Bernardino Ring-necked Snake
D. p. pulchellus - Coral-bellied Ring-necked Snake
D. p. regalis - Regal Ring-necked Snake
"Fontanella et al. (2017, Zoological Journal of the Linnean Society 182: 444– 458) evaluated the contact zone between two of the lineages (D. p. edwardsi North and D. p. edwardsi South). Morphological differences between these two lineages were clinal, whereas mtDNA sequence data were discrete but with zones of secondary contact. Fontanella et al. (2021, Biological Journal of the Linnean Society 133: 105-119) used combined morphometric and genomic data for Pacific Coast populations and determined that those populations represented three subspecific taxa. They synonymized D. p. occidentalis and D. p. vandenburghi with D. p. amabilis, and D. p. similis with D. p. modestus. Otherwise, our arrangement follows the traditional subspecies groupings."
(Nicholson, K. E. (ed.). 2025 SSAR Scientific and Standard English Names List)
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
Alternate and Previous Names (Synonyms)
Diadophis punctatus amabilis - Pacific Ring-necked Snake (Hansen and Shedd 2025)
Diadophis punctatus - Ring-necked Snake (no subspecies) (Stebbins & McGinnis 2018)
Diadophis punctatus - Ring-necked Snake (no subspecies) (Stebbins & McGinnis 2012)
Diadophis punctatus - Ring-necked Snake (no subspecies) (Stebbins 2003)
Diadophis punctatus amabilis - Pacific Ringneck Snake (Stebbins 1966, 1985)
Diadophis punctatus amabilis (Wright & Wright 1957)
Diadophis amabilis amabilis - (Stebbins 1954)
Diadophis amabilis - Western Ring-necked Snake (Diadophis pulchellus; Diadophis punctatus pulchellus; Diadophis punctatus amabilis; Diadophis amabilis pulchellus; Coronella amabilis; Ablabs punctatus; Coluber punctatus; Diadophis punctatus. California Ring-necked Snake; Red-bellied Snake; Spotted Ring Snake) (Grinnell and Camp 1917)
Diadophis amabilis amabilis - Western ring-necked snake (Ditmars 1907)
Western ring-neck snake (Van Denburgh 1897)
California ring-necked snake; pacific ring-neck snake; red-bellied snake; spotted ring neck - (Cooper 1869)
|
| Conservation Issues (Conservation Status) |
| None |
|
| Taxonomy |
| Family |
Colubridae |
Colubrids |
Oppel, 1811 |
| Genus |
Diadophis |
Ring-necked Snakes |
Baird and Girard, 1853 |
| Species |
punctatus |
Ring-necked Snake |
(Linnaeus, 1766) |
Subspecies
|
amabilis |
Pacific Ring-necked Snake |
Baird and Girard, 1853 |
|
Original Description |
Diadophis punctatus - (Linnaeus, 1766) - Syst. Nat., 12th ed., Vol. 1, p. 376
Diadophis punctatus amabilis - Baird and Girard, 1853 - Cat. N.
from Original Description Citations for the Reptiles and Amphibians of North America © Ellin Beltz
|
|
Meaning of the Scientific Name |
Diadophis - Latin - diadema = crown + Greek -ophis = snake -- "generally with a light ring on the occipital region."
punctatus - Latin = dotted - refers to spotted belly of species
amabilis - Latin = lovely
from Scientific and Common Names of the Reptiles and Amphibians of North America - Explained © Ellin Beltz
|
|
Related or Similar California Snakes |
D. p. modestus - San Bernardino Ring-necked Snake
D. p. occidentalis - Northwestern Ring-necked Snake
D. p. pulchellus - Coral-bellied Ring-necked Snake
D. p. regalis - Regal Ring-necked Snake
D. p. similis - San Diego Ring-necked Snake
D. p. vandenburgii - Monterey Ring-necked Snake
C. tenuis - Sharp-tailed Snake
T. hobartsmithi - Southwestern Black-headed Snake
T. planiceps - California Black-headed Snake
|
|
More Information and References |
California Department of Fish and Wildlife
Hansen, Robert W. and Shedd, Jackson D. California Amphibians and Reptiles. (Princeton Field Guides.) Princeton University Press, 2025.
Stebbins, Robert C., and McGinnis, Samuel M. Field Guide to Amphibians and Reptiles of California: Revised Edition (California Natural History Guides) University of California Press, 2012.
Stebbins, Robert C. California Amphibians and Reptiles. The University of California Press, 1972.
Flaxington, William C. Amphibians and Reptiles of California: Field Observations, Distribution, and Natural History. Fieldnotes Press, Anaheim, California, 2021.
Nicholson, K. E. (ed.). 2025. Scientific and Standard English Names of Amphibians and Reptiles of North America North of Mexico, with Comments Regarding Confidence in Our Understanding. Ninth Edition. Society for the Study of Amphibians and Reptiles. [SSAR] 87pp.
Samuel M. McGinnis and Robert C. Stebbins. Peterson Field Guide to Western Reptiles & Amphibians. 4th Edition. Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company, 2018.
Stebbins, Robert C. A Field Guide to Western Reptiles and Amphibians. 3rd Edition. Houghton Mifflin Company, 2003.
Behler, John L., and F. Wayne King. The Audubon Society Field Guide to North American Reptiles and Amphibians. Alfred A. Knopf, 1992.
Robert Powell, Roger Conant, and Joseph T. Collins. Peterson Field Guide to Reptiles and Amphibians of Eastern and Central North America. Fourth Edition. Houghton Mifflin Harcourt, 2016.
Powell, Robert., Joseph T. Collins, and Errol D. Hooper Jr. A Key to Amphibians and Reptiles of the Continental United States and Canada. The University Press of Kansas, 1998.
Bartlett, R. D. & Patricia P. Bartlett. Guide and Reference to the Snakes of Western North America (North of Mexico) and Hawaii. University Press of Florida, 2009.
Bartlett, R. D. & Alan Tennant. Snakes of North America - Western Region. Gulf Publishing Co., 2000.
Brown, Philip R. A Field Guide to Snakes of California. Gulf Publishing Co., 1997.
Ernst, Carl H., Evelyn M. Ernst, & Robert M. Corker. Snakes of the United States and Canada. Smithsonian Institution Press, 2003.
Taylor, Emily. California Snakes and How to Find Them. Heyday, Berkeley, California. 2024.
Wright, Albert Hazen & Anna Allen Wright. Handbook of Snakes of the United States and Canada. Cornell University Press, 1957.
Fontanella , Frank M., Chris R. Feldman, Mark E. Siddall, & Frank T. Burbrink. Phylogeography of Diadophis punctatus: Extensive lineage diversity and repeated patterns of historical demography in a trans-continental snake. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution 46 (2008) 1049–1070. 2008.
Frank M. Fontanella, Emily Miles, and Polly Strott. Integrated analysis of the ringneck snake Diadophis punctatus complex (Colubridae: Dipsadidae) in a biodiversity hotspot provides the foundation for conservation reassessment. Biological Journal of the Linnean Society, 2021, XX, 1–15
Joseph Grinnell and Charles Lewis Camp. A Distributional List of the Amphibians and Reptiles of California. University of California Publications in Zoology Vol. 17, No. 10, pp. 127-208. July 11, 1917.
|
|
|
The following conservation status listings for this animal are taken from the April 2024 State of California Special Animals List and the April 2024 Federally Listed Endangered and Threatened Animals of California list (unless indicated otherwise below.) Both lists are produced by multiple agencies every year, and sometimes more than once per year, so the conservation status listing information found below might not be from the most recent lists. To make sure you are seeing the most recent listings, go to this California Department of Fish and Wildlife web page where you can search for and download both lists:
https://www.wildlife.ca.gov/Data/CNDDB/Plants-and-Animals.
A detailed explanation of the meaning of the status listing symbols can be found at the beginning of the two lists. For quick reference, I have included them on my Special Status Information page.
If no status is listed here, the animal is not included on either list. This most likely indicates that there are no serious conservation concerns for the animal. To find out more about an animal's status you can also go to the NatureServe and IUCN websites to check their rankings.
Check the current California Department of Fish and Wildlife sport fishing regulations to find out if this animal can be legally pursued and handled or collected with possession of a current fishing license. You can also look at the summary of the sport fishing regulations as they apply only to reptiles and amphibians that has been made for this website.
This snake is not included on the Special Animals List, which indicates that there are no significant conservation concerns for it in California.
|
| Organization |
Status Listing |
Notes |
| NatureServe Global Ranking |
|
|
| NatureServe State Ranking |
|
|
| U.S. Endangered Species Act (ESA) |
None |
|
| California Endangered Species Act (CESA) |
None |
|
| California Department of Fish and Wildlife |
None |
|
| Bureau of Land Management |
None |
|
| USDA Forest Service |
None |
|
| IUCN |
|
|
|
|






































































